Perch Anatomy Guide Answers
Figure 5 – Internal Perch Anatomy. Questions & Observations: 1. Are both jaws of the fish equally movable? Explain your answer. Does the perch have eyelids? How many gills are located on each side of the perch? What covering protects them? What is the function of the gill rakers? Explain how gas exchange occurs at the gills.
Widely thought to be the greatest player of all time, Chicago Bulls legend Michael Jordan has proven himself to be as good a businessman as he was a ball player, boasting an incredibly large net worth that was only really made after the player hung up his Jordans. In a career spanning nearly two decades, Jordan set many NBA records and won six titles with the Chicago Bulls. He was a five-time NBA MVP, a six-time NBA Finals MVP, 14-time NBA All-Star and member of the 50th Anniversary All-Time Team. Jordan was so prolific and had such a massive impact that upon his final retirement in 2003, the Miami Heat retired his famous number 23 jersey, despite the fact the player never played for the team.
Jordan led the Chicago Bulls to six NBA titles, winning three Championships in a row twice Even during his playing career, Jordan was already being viewed as the greatest of all time. ‘There’s Michael Jordan and then there is the rest of us,’ NBA and LA Lakers legend Magic Johnson once said, while Larry Bird said: ‘God disguised as Michael Jordan.’ Here is all you need to know about Michael Jordan including who he is, his NBA career and stats, what is his net worth and how much he earns today. Who is Michael Jordan? Born in Brooklyn, but raised in Wilmington, North Carolina, Michael Jordan attended the local Laney High school, where he initially failed to make the varsity basketball team as a 5ft 11 sophomore. However, over the summer ensured that Jordan’s prolific talent didn’t remain hidden for long.
He ended his high school basketball career as an All-American. He chose a basketball scholarship at University of North Carolina and played his way into the university’s Tar Heel basketball program mythology when he made the game-winning jumper for his university against Georgetown in the 1982 NCAA championship game, with just 18 seconds on the clock; the game ended 63-62. He was voted Sporting News’s College Player of the Year both as a sophomore and as a junior. In 1984, Jordan was the third overall draft pick, being selected by the Chicago Bulls.

Jordan immediately became a fan favourite at the Chicago Stadium and attendances actually began to increase, with people turning up to see the new wunderkind. He ended his first season as the Rookie of the Year. A foot break early in the second season saw Jordan miss 64 games only to return later in the season and score a record 63 points in an NBA playoff game.
It was in his third season, 1986-87, that Jordan truly got up and running in the NBA. It was the first of seven consecutive seasons that Jordan scored an average of 30 points or more per game.
That season also saw Jordan set the record for scoring 23 consecutive points in a game, as well as scoring 40 points or more in nine games in a row. Between 1987 and 1990, during which time Jordan’s Bulls lost to the Detroit Pistons in the NBA playoffs, Jordan led his team to three consecutive NBA titles, firmly earning himself a place in NBA lore. However, the shocking murder of his father and idol in 1993 contributed to Jordan’s surprise decision to retire in October of that year. He then surprised the sporting world again by signing up to Minor League Baseball, before returning to NBA and the Bulls in 1995, simply saying: ‘I’m back’. His return pushed the struggling Bulls to another ‘three-peat’—winning the NBA title three times in a row, with Jordan sealing the threepeat in the 1997/98 season with a game-winning shot against the Utah Jazz with just 6.6 seconds on the clock. Jordan retired for the second time in 1999 only to return to the NBA again in 2001 for two years.
He finally retired for good in April 2003. A post shared by (@jumpman23) on Feb 6, 2018 at 1:41pm PST What is Michael Jordan’s net worth? Michael Jordan’s net worth is estimated to be $1.7 billion (£1.2bn), according to. The basketball legend earnt the bulk of his staggering net worth after his playing career ended.
According to Sportrac, Jordan just under $90 million during his NBA career. However, despite being retired, Jordan is thought to make much more than any active NBA player, including LeBron James, Kevin Durant or Stephen Curry. According to Forbes, Jordan $100 million a year from his Nike Air Jordan royalties. A post shared by (@steelworksunlimited) on Mar 6, 2017 at 2:28pm PST LeBron only makes $90 million in total, including his salary and endorsements. Jordan’s Air Jordan sneakers reportedly generate $2 billion a year, not a bad return for Nike, who Jordan in 1984 for just $250,000. After Jordan retired, he gradually moved into franchise ownership and operation oversight, ultimately buying the Charlotte Hornets for $175 million in 2010.

As of 2018, the NBA team is worth $1.05 billion and Jordan owns 90 per cent of it. Jordan’s incredible wealth has allowed the legend to purchase things like a private jet that has the famous Air Jordan logo on it, as well as his iconic 23 jersey number and initials. He also owns a $13 million home in Florida and is building his own golf course called Grove XXIII, which will open in 2019. Jordan also owns multi-million properties in Charlotte and Chicago.
Perch Dissection Introduction and Pre-Lab Information: The fish in the class Osteichthyes have bony skeletons. There are three groups of the bony fish - ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, and the lung fish. The perch is an example of a ray-finned fish. Its fins have spiny rays of cartilage &/or bone to support them. Fins help the perch to move quickly through the water and steer without rolling.
Click for more information about the fins found on the perch and their functions. The perch also has a streamline body shape that makes it well adapted for movement in the water.
All ray-finned fish have a swim bladder that gives the fish buoyancy allowing them to sink or rise in the water. The swim bladder also regulates the concentration of gases in the blood of the fish. Perch have powerful jaws and strong teeth for catching and eating prey. Yellow perch are primarily bottom feeders with a slow deliberate bite.
They eat almost anything, but prefer minnows, insect larvae, plankton, and worms. Perch move about in schools, often numbering in the hundreds. The scientific name for the yellow perch, most often used in dissection, is Perca flavescens (Perca means 'dusky'; flavescens means 'becoming gold colored'). The sides of the yellow perch are golden yellow to brassy green with six to eight dark vertical saddles and a white to yellow belly. Along the side of the fish is the lateral line. Click to learn more about the lateral line and its functions.
Yellow perch have many small teeth, but no large canines. Yellow perch spawn from mid-April to early May by depositing their eggs over vegetation or the water bottom, with no care given. The eggs are laid in large gelatinous adhesive masses. At this time, you are to answer the Pre-Lab Questions on your Perch Dissection Review Worksheet.
Materials: Preserved perch, dissecting tray, scalpel, scissors, forceps, Brock microscope, dissecting pins, length of string, ruler or meter stick Procedure (External Anatomy):. Obtain a perch & rinse off the excess preservative.
Place the perch in your dissecting pan. Use your string and ruler or meter stick to determine the total length, fork length, and girth of your fish. Record this in Table 1. Locate the 3 body regions of the perch - head, trunk, and tail.
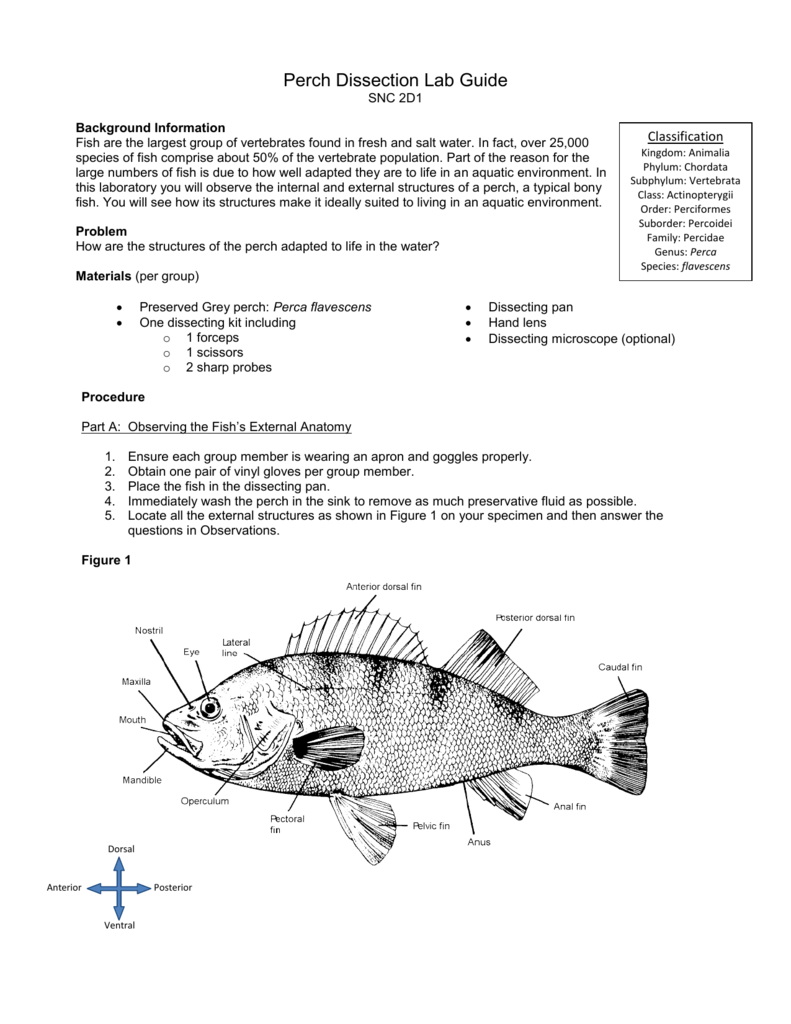
Label these on Figure 1. Open the perch's mouth and observe its bony jaws. The upper jaw is fixed and will not move. The mandible is the moveable part of its jaw. Locate and label the upper jaw or maxilla and the lower jaw or mandible. Feel the inside of the mouth for the teeth. Locate the tongue & teeth on Figure 1.
Open the mouth wider and use a probe to reach back to the gill chamber. Find the lateral line on the side of your perch. Label this line on Figure 1. Locate the nostrils and label on Figure 1. Locate and note the location of the eyes. Label on Figure 1. Find the bony covering on each side of the fish's head called the operculum.
The opercula cover & protect the gills. Label this on Figure 1. Figure 1 diagram on your lab review should be labeled with the following items:. head region. trunk region. tail region.
maxilla. mandible. nostril. eye.
operculum. lateral line. Use a probe to lift the operculum and observe the gills. Note their color. Use a scissors to cut away one operculum to view the gills. There should be two pairs of gills on each side of the perch (4 total gills).
Find the gill slits or spaces between the gills. Click to find more information about gill rakers. Use your scalpel to carefully cut out one gill.
Perch Anatomy Quiz
Find the cartilage support called the gill arch and the soft gill filaments that make up each gill. Label the parts of the gill in Figure 2 on your lab review. Fish Gill Anatomy The gill structure on the right is the one that will be found in your perch. Observe the different fins on the perch. Locate the pectoral, dorsal, pelvic, anal, and caudal fins. Note whether the fin has spines. Complete Table 2.
With the information about the fins. Locate the anus on the perch anterior to the anal fin. In the female, the anus is in front of the genital pore, and the urinary pore is located behind the genital pore. The male has only one pore (urogenital pore) behind the anus. Determine the sex of your perch. Record this on your lab review worksheet.
Use forceps to remove a few scales from your fish. Observe the scales under the Brock microscope. Sketch what you see on your lab review worksheet. Close-up View of a Perch Scale The age of the fish the scale above was taken from is 7 years. Count the growth rings on your scale to tell the age of your fish. (Hint: each ring represents one year's growth.) Click for more information about fish scale growth rings. Click for more information about fish scales in general.
Procedure (Internal Anatomy):. Use dissecting pins to secure the fish to the dissecting pan.
Use scissors to make the cuts through skin and muscle shown below. Cut Lines for Internal dissection. After making the cuts, carefully lift off the flap of skin and muscle to expose the internal organs in the body cavity. Locate the cream colored liver in the front of the body cavity. Also locate the gall bladder between the lobes of the liver.
Label these on Figure 3 on your lab review worksheet. Remove the gall bladder & liver to observe the short esophagus attached to the stomach. Label the stomach on Figure 3 on your lab review worksheet. At the posterior end of the stomach are the coiled intestines.
Locate and then label these on Figure 3 on your lab review worksheet. Find the small reddish brown spleen near the stomach and label this on Figure 3 on your lab review worksheet. Below the operculum, are the bony gill rakers. Locate these & them label them on Figure 3. In front of the liver & behind the gill rakers is the pericardial cavity containing the heart. The heart of a fish only has 2 chambers - an atrium & and a ventricle. Locate the heart & label it on Figure 3.
In the upper part of the body below the lateral line is the swim bladder. Suzuki rmx 250 94 manual. This sac has a thin wall and gives the fish buoyancy. Label the swim bladder on Figure 3.
Below the swim bladder are the gonads, testes or ovaries. In a female, these may be filled with eggs. Label the gonads on Figure 3. Find the 2 long, dark kidneys in the posterior end of the perch.
These filter wastes from the blood. Label the kidneys in Figure 3. Wastes exit the body through the vent located on the ventral side of the perch. Label this structure on Figure 3. Complete the Post-Lab Questions on your Perch Dissection Review Worksheet Cl ick for the Perch Dissection Lab Companion.